Table of Contents
What is included in this blog post?
Dynamodb is a widely used db service and as a cloud DBA/DBE you may need to support Dynamodb tables in addition to RDS , Aurora etc.. We are starting “Dynamodb for DBAs” series with this post. This blog post helps you in calculating RCUs and WCUs (Read Capacity Units and Write Capacity Units ) for any given scenario. We also compare two different modes – on demand and provisioned capacity
Ondemand Vs Provisioned capacity
There are two ways to handle capacity in Dynamodb – Ondemand and Provisioned . Ondemand is generally good when you have unpredictable workloads and Provisioned is generally good for predictable workloads
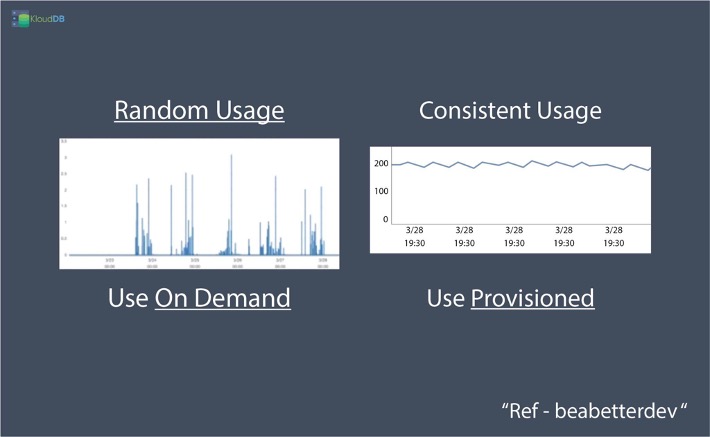
If you see in below diagram , ondemand is better for random and unpredictable traffic patterns whereas provisioned is better for predictable and consistent traffic patterns Ref – BeABetterDev
RCUs and WCUs - Dynamodb units
One RCU is :
A strongly consistent read request of an item up to 4 KB requires one read request unit.An eventually consistent read request of an item up to 4 KB requires 1/2 read request unit.
So if you use eventual consistency you will be charged less (compared to strong consistency)

One WCU is :
One write request unit represents one write for an item up to 1 KB in size

Strong consistency Vs Eventual consistency
With strong consistency you get the latest data whereas with eventual consistency there is a chance of reading stale data sometimes
RCU Scenario 1 - Avg item size is 1KB and 50 items/sec are read
In this particular scenario item size is 1KB and the estimated reads/second is 50 items/sec . For this particular scenario consumed RCUs will be 50 for strong consistency and 25 for Eventual consistency
Here is how the calculation is done –
- Average item size / 4KB (Ceiling applied) = 1KB /4KB = 1 RCU
- Multiply the number from step 1(above step) * Items/sec = 1 * 50 = 50 RCUs(for strong consistency)
Since it is 50 RCUs for strong consistency , Eventual will be half of 50 which is 25 RCUs
RCU Scenario 2 - Avg item size is 9KB and 50 items/sec are read
In this particular scenario item size is 9KB and the estimated reads/second is 50 items/sec . For this particular scenario consumed RCUs will be 100 for strong consistency and 75 for Eventual consistency
Here is how the calculation is done –
- Average item size / 4KB (Ceiling applied) = 9KB /4KB => 2.25 => 3 (Ceiling applied)
- Multiply the number from step 1(above step) * Items/sec = 3 * 50 = 150 RCUs(for strong consistency)
Since it is 150 RCUs for strong consistency , Eventual will be half of 150 which is 75 RCUs
RCU Scenario 3 - Avg item size is 11KB and 25 items/sec are read
In this particular scenario item size is 11KB and the estimated reads/second is 25 items/sec . For this particular scenario consumed RCUs will be 75 for strong consistency and 38 for Eventual consistency
Here is how the calculation is done –
- Average item size / 4KB (Ceiling applied) = 11KB /4KB => 2.75 => 3 (Ceiling applied)
- Multiply the number from step 1(above step) * Items/sec = 3 * 25 = 75 RCUs(for strong consistency)
Since it is 75 RCUs for strong consistency , Eventual will be half of 75 which is 38 RCUs
RCU Scenario 4 - Avg item size is 8KB and 50 items/sec are read
In this particular scenario item size is 8KB and the estimated reads/second is 50 items/sec . For this particular scenario consumed RCUs will be 100 for strong consistency and 50 for Eventual consistency
Here is how the calculation is done –
- Average item size / 4KB (Ceiling applied) = 8KB /4KB => 2 => 2 (Ceiling applied)
- Multiply the number from step 1(above step) * Items/sec = 2 * 50 = 100 RCUs(for strong consistency)
Since it is 100 RCUs for strong consistency , Eventual will be half of 100 which is 50 RCUs
RCU Scenario 5 - Avg item size is 123KB and 25 items/sec are read
In this particular scenario item size is 123KB and the estimated reads/second is 25 items/sec . For this particular scenario consumed RCUs will be 775 for strong consistency and 388 for Eventual consistency
Here is how the calculation is done –
- Average item size / 4KB (Ceiling applied) = 123 / 4 => 30.75 => 31 (Ceiling applied)
- Multiply the number from step 1(above step) * Items/sec ==> 31 * 25 =>775 RCUs(for strong consistency)
Since it is 775 RCUs for strong consistency , Eventual will be half of 775 which is 388 RCUs
WCU Scenario 1 - Avg item size is 8KB and 50 items/sec are written
In this particular scenario item size is 8KB and the estimated writes is 50 items/sec . For this particular scenario consumed WCUs will be 100 for strong consistency and 100 for Eventual consistency (same unlike RCUs)
Strong :
Average item size / 1KB (Ceiling applied) = 8 / 1 => 8 => 8 (Ceiling applied)
Number obtained in #1 * Number of items/sec => 8 * 50 =>400
Eventual :
Same as strong = 400
WCU Scenario 2 - Avg item size is 11KB and 50 items/sec are written
In this particular scenario item size is 11KB and the estimated writes is 50 items/sec . For this particular scenario consumed WCUs will be 550 for strong consistency and 550 for Eventual consistency (same unlike RCUs)
Strong :
Average item size / 1KB (Ceiling applied) = 11 / 1 => 11 => 11 (Ceiling applied)
Number obtained in #1 * Number of items/sec => 11 * 50 => 550
Eventual :
Same as strong = 550
Free utility to calculate based on the json payload
Below tool can be used to automatically calculate capacity units (JSON representation of Dynamodb item as input)
Conclusion
Dynamodb is widely used these days and it is important to keep track of RCUs and WCUs consumed by your app
